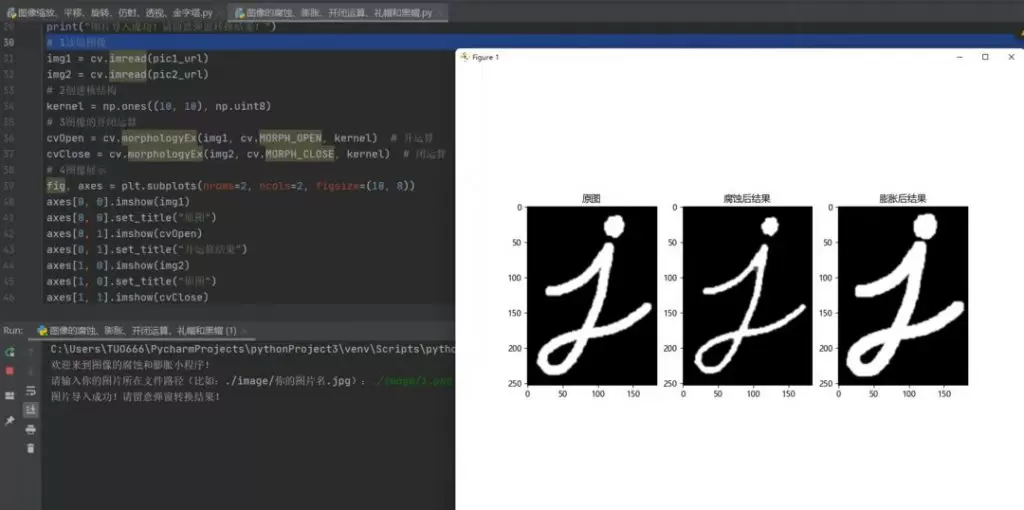
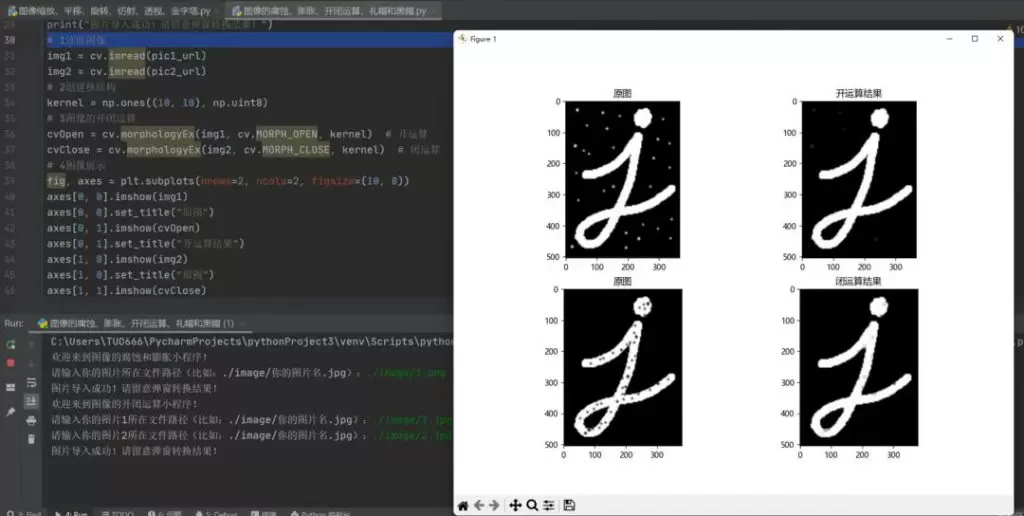
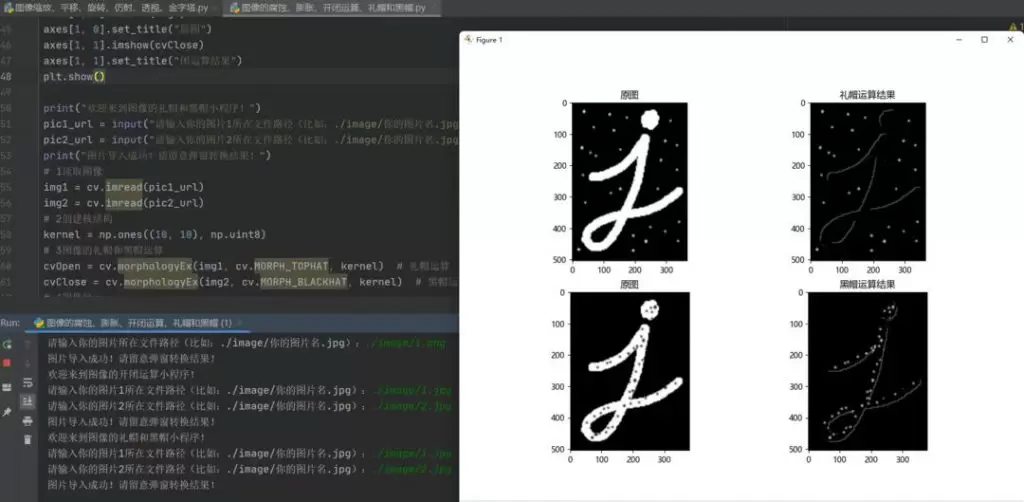
import numpy as npimport c<a href="https://www.knrjk.com/tag/1479" target="_blank">v</a>2 as cvimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 1读取图像pic_url = './images/pic1.png'img = cv.imread(pic_url)# 2创建核结构kernel = np.ones((5, 5), np.uint8)# 3图像腐<a href="https://www.knrjk.com/tag/6505" target="_blank">蚀</a>和膨胀erosion = cv.erode(img, kernel) # 腐蚀dilate = cv.dilate(img, kernel) # 膨胀# 4图像展示plt.rc("font", family='Microsoft YaHei')fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=3, figsize=(10, 8), dpi=100)axes[0].imshow(img)axes[0].set_title("原图")axes[1].imshow(erosion)axes[1].set_title("腐蚀后结果")axes[2].imshow(dilate)axes[2].set_title("膨胀后结果")plt.show()# 1读取图像pic1 = './images/pic1.jpg'pic2 = './images/pic2.jpg'img1 = cv.imread(pic1)img2 = cv.imread(pic2)# 2创建核结构kernel = np.ones((10, 10), np.uint8)# 3图像的开闭运算cvOpen = cv.morphologyEx(img1, cv.MORPH_OPEN, kernel) # 开运算cvClose = cv.morphologyEx(img2, cv.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel) # 闭运算# 4图像展示fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 8))axes[0, 0].imshow(img1)axes[0, 0].set_title("原图")axes[0, 1].imshow(cvOpen)axes[0, 1].set_title("开运算结果")axes[1, 0].imshow(img2)axes[1, 0].set_title("原图")axes[1, 1].imshow(cvClose)axes[1, 1].set_title("闭运算结果")plt.show()# 1读取图像img1 = cv.imread(pic1)img2 = cv.imread(pic2)# 2创建核结构kernel = np.ones((10, 10), np.uint8)# 3图像的礼帽和黑帽运算cvOpen = cv.morphologyEx(img1, cv.MORPH_TOPHAT, kernel) # 礼帽运算cvClose = cv.morphologyEx(img2, cv.MORPH_BLACKHAT, kernel) # 黑帽运算# 4图像显示fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 8))axes[0, 0].imshow(img1)axes[0, 0].set_title("原图")axes[0, 1].imshow(cvOpen)axes[0, 1].set_title("礼帽运算结果")axes[1, 0].imshow(img2)axes[1, 0].set_title("原图")axes[1, 1].imshow(cvClose)axes[1, 1].set_title("黑帽运算结果")plt.show()import numpy as np import c<a href="https://www.knrjk.com/tag/1479" target="_blank">v</a>2 as cv import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 1读取图像 pic_url = './images/pic1.png' img = cv.imread(pic_url) # 2创建核结构 kernel = np.ones((5, 5), np.uint8) # 3图像腐<a href="https://www.knrjk.com/tag/6505" target="_blank">蚀</a>和膨胀 erosion = cv.erode(img, kernel) # 腐蚀 dilate = cv.dilate(img, kernel) # 膨胀 # 4图像展示 plt.rc("font", family='Microsoft YaHei') fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=3, figsize=(10, 8), dpi=100) axes[0].imshow(img) axes[0].set_title("原图") axes[1].imshow(erosion) axes[1].set_title("腐蚀后结果") axes[2].imshow(dilate) axes[2].set_title("膨胀后结果") plt.show() # 1读取图像 pic1 = './images/pic1.jpg' pic2 = './images/pic2.jpg' img1 = cv.imread(pic1) img2 = cv.imread(pic2) # 2创建核结构 kernel = np.ones((10, 10), np.uint8) # 3图像的开闭运算 cvOpen = cv.morphologyEx(img1, cv.MORPH_OPEN, kernel) # 开运算 cvClose = cv.morphologyEx(img2, cv.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel) # 闭运算 # 4图像展示 fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 8)) axes[0, 0].imshow(img1) axes[0, 0].set_title("原图") axes[0, 1].imshow(cvOpen) axes[0, 1].set_title("开运算结果") axes[1, 0].imshow(img2) axes[1, 0].set_title("原图") axes[1, 1].imshow(cvClose) axes[1, 1].set_title("闭运算结果") plt.show() # 1读取图像 img1 = cv.imread(pic1) img2 = cv.imread(pic2) # 2创建核结构 kernel = np.ones((10, 10), np.uint8) # 3图像的礼帽和黑帽运算 cvOpen = cv.morphologyEx(img1, cv.MORPH_TOPHAT, kernel) # 礼帽运算 cvClose = cv.morphologyEx(img2, cv.MORPH_BLACKHAT, kernel) # 黑帽运算 # 4图像显示 fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 8)) axes[0, 0].imshow(img1) axes[0, 0].set_title("原图") axes[0, 1].imshow(cvOpen) axes[0, 1].set_title("礼帽运算结果") axes[1, 0].imshow(img2) axes[1, 0].set_title("原图") axes[1, 1].imshow(cvClose) axes[1, 1].set_title("黑帽运算结果") plt.show()import numpy as np import cv2 as cv import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 1读取图像 pic_url = './images/pic1.png' img = cv.imread(pic_url) # 2创建核结构 kernel = np.ones((5, 5), np.uint8) # 3图像腐蚀和膨胀 erosion = cv.erode(img, kernel) # 腐蚀 dilate = cv.dilate(img, kernel) # 膨胀 # 4图像展示 plt.rc("font", family='Microsoft YaHei') fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=3, figsize=(10, 8), dpi=100) axes[0].imshow(img) axes[0].set_title("原图") axes[1].imshow(erosion) axes[1].set_title("腐蚀后结果") axes[2].imshow(dilate) axes[2].set_title("膨胀后结果") plt.show() # 1读取图像 pic1 = './images/pic1.jpg' pic2 = './images/pic2.jpg' img1 = cv.imread(pic1) img2 = cv.imread(pic2) # 2创建核结构 kernel = np.ones((10, 10), np.uint8) # 3图像的开闭运算 cvOpen = cv.morphologyEx(img1, cv.MORPH_OPEN, kernel) # 开运算 cvClose = cv.morphologyEx(img2, cv.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel) # 闭运算 # 4图像展示 fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 8)) axes[0, 0].imshow(img1) axes[0, 0].set_title("原图") axes[0, 1].imshow(cvOpen) axes[0, 1].set_title("开运算结果") axes[1, 0].imshow(img2) axes[1, 0].set_title("原图") axes[1, 1].imshow(cvClose) axes[1, 1].set_title("闭运算结果") plt.show() # 1读取图像 img1 = cv.imread(pic1) img2 = cv.imread(pic2) # 2创建核结构 kernel = np.ones((10, 10), np.uint8) # 3图像的礼帽和黑帽运算 cvOpen = cv.morphologyEx(img1, cv.MORPH_TOPHAT, kernel) # 礼帽运算 cvClose = cv.morphologyEx(img2, cv.MORPH_BLACKHAT, kernel) # 黑帽运算 # 4图像显示 fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(10, 8)) axes[0, 0].imshow(img1) axes[0, 0].set_title("原图") axes[0, 1].imshow(cvOpen) axes[0, 1].set_title("礼帽运算结果") axes[1, 0].imshow(img2) axes[1, 0].set_title("原图") axes[1, 1].imshow(cvClose) axes[1, 1].set_title("黑帽运算结果") plt.show()
THE END

